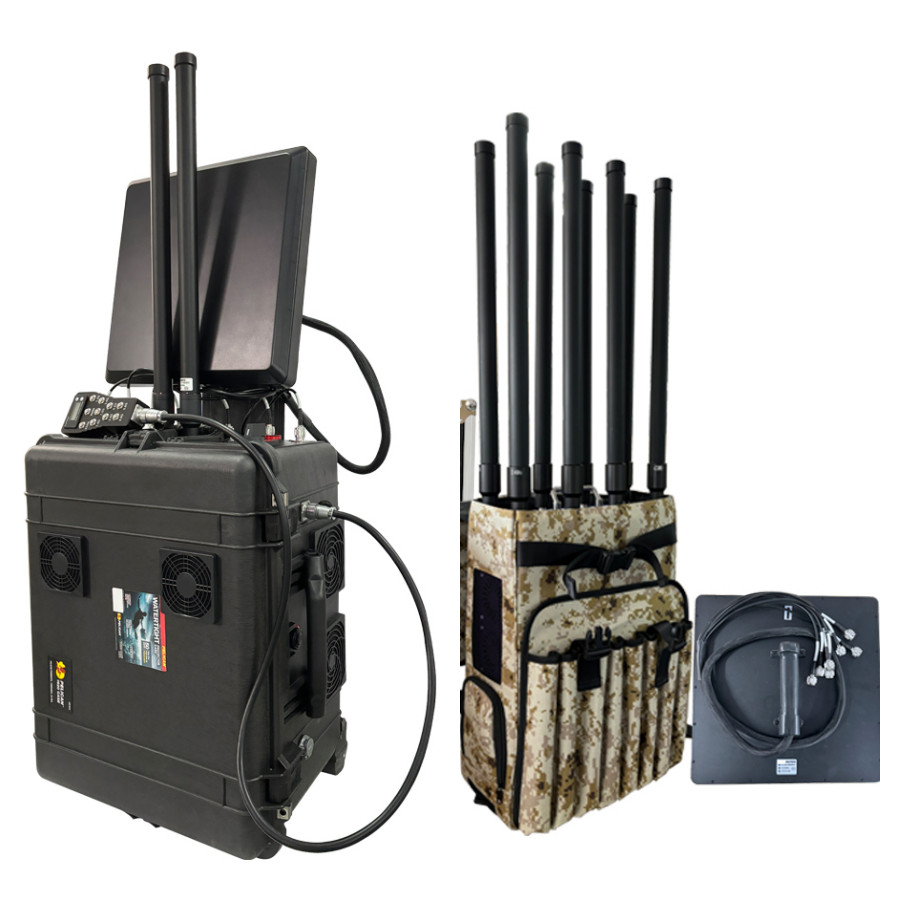
Modern security threats increasingly involve unauthorized drones infiltrating restricted airspace, requiring sophisticated countermeasures to protect sensitive facilities and public safety. A directional antenna represents a critical component in advanced anti-drone systems, offering precise signal disruption capabilities that conventional omnidirectional solutions cannot match. These specialized antennas provide focused electromagnetic energy transmission, enabling security personnel to target specific aerial threats while minimizing interference to surrounding communication systems and legitimate aircraft operations.
The strategic implementation of directional antennas in drone jamming systems has revolutionized counter-UAV operations across military installations, airports, government buildings, and critical infrastructure sites. Unlike traditional broadcasting methods that disperse signal energy across wide areas, directional antennas concentrate electromagnetic power toward specific coordinates, delivering maximum disruption efficiency while maintaining operational discretion. This targeted approach ensures that drone operators lose control over their vehicles without affecting nearby cellular networks, WiFi systems, or emergency communication channels that rely on similar frequency bands.
Security professionals increasingly recognize that effective drone neutralization requires precision rather than brute force signal saturation. A properly configured directional antenna system can disable threatening drones at distances exceeding several kilometers while using significantly less power than omnidirectional alternatives. This efficiency translates to reduced operational costs, extended battery life for portable systems, and decreased likelihood of detection by sophisticated adversaries employing counter-surveillance techniques.
Technical Advantages of Directional Antenna Systems
Enhanced Signal Focus and Power Concentration
Directional antennas achieve superior performance through their ability to concentrate electromagnetic energy into narrow beam patterns, typically ranging from 10 to 60 degrees depending on specific design requirements. This focused transmission creates higher effective radiated power in the target direction while substantially reducing signal spillage into unintended areas. The mathematical relationship between antenna gain and beamwidth demonstrates that narrower beam patterns produce higher directional gains, often exceeding 15-20 dBi for high-performance models used in professional counter-drone applications.
The concentrated signal strength enables operators to overcome drone communication protocols even when targeting aircraft equipped with robust receivers or frequency-hopping capabilities. Modern commercial drones often employ spread-spectrum technologies and error-correction algorithms designed to maintain connectivity in challenging RF environments. However, the intense signal density produced by a well-positioned directional antenna can overwhelm these protective measures, forcing immediate loss of control link and triggering automated return-to-home sequences or emergency landing protocols built into most consumer and commercial drone platforms.
Reduced Interference and Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory agencies worldwide impose strict limitations on electromagnetic emissions to prevent interference with licensed communication services, aviation systems, and emergency response networks. Directional antennas naturally comply with these requirements by directing energy away from protected frequency users while concentrating jamming power where it provides maximum effectiveness against unauthorized drones. This compliance advantage becomes particularly important when deploying counter-UAV systems near airports, hospitals, or other locations where communication reliability remains paramount for public safety operations.
The reduced interference footprint also enables covert operations where security teams must neutralize drone threats without alerting nearby observers to active countermeasures. Traditional omnidirectional jammers often create widespread communication disruptions that immediately signal defensive activities to potential adversaries. In contrast, a precisely aimed directional antenna can disable target drones while leaving surrounding electronic devices completely unaffected, maintaining operational security and preventing escalation of security incidents.
Operational Benefits in Real-World Applications
Improved Range and Coverage Efficiency
Field deployments consistently demonstrate that directional antenna systems achieve significantly greater effective ranges compared to omnidirectional alternatives operating at identical power levels. The improved range capability stems from the antenna's ability to focus available transmitter power into the specific direction where drone threats typically approach protected facilities. Most security installations can predict likely drone approach vectors based on terrain features, population centers, and existing flight restrictions, enabling optimal antenna positioning for maximum coverage of high-risk zones.
Extended range capabilities prove especially valuable when protecting large facilities such as military bases, power plants, or transportation hubs where early threat detection and neutralization prevent drones from reaching sensitive areas. The ability to engage targets at distances exceeding 2-3 kilometers provides security teams with adequate response time to assess threat levels, implement additional countermeasures if necessary, and coordinate with law enforcement agencies responsible for investigating unauthorized drone operations in restricted airspace.
Selective Targeting and Threat Assessment
Modern directional antenna systems integrate with sophisticated radar and electro-optical detection networks, enabling operators to identify and engage specific targets while ignoring authorized aircraft operating in the same general area. This selective engagement capability reduces false alarms and prevents accidental interference with legitimate aviation activities, medical helicopters, or law enforcement aircraft that may operate near protected facilities during routine operations or emergency responses.
The precision targeting capability also supports graduated response protocols where security personnel can disable specific drone functions rather than causing immediate crashes that might result in property damage or injury to bystanders. Advanced directional antenna systems can selectively jam GPS navigation signals while leaving control links intact, forcing drones to hover in place until operators manually retrieve them. Alternatively, jamming only control frequencies while preserving GPS functionality triggers automatic return-to-home sequences that lead investigating authorities directly to drone operators.
Integration with Comprehensive Security Systems
Multi-Layer Defense Architecture
Effective counter-drone operations require integration of directional antenna systems within broader security architectures that combine detection, identification, tracking, and neutralization capabilities. The directional antenna serves as the primary effector component, working in coordination with radar systems for long-range detection, electro-optical sensors for visual identification, and radio frequency analyzers for signal intelligence gathering. This multi-layer approach ensures that security teams can detect approaching threats early, assess their intentions, and deploy appropriate countermeasures before unauthorized drones reach critical areas.
Integration protocols typically involve automated handoff procedures where detection systems provide targeting data directly to directional antenna controllers, enabling rapid engagement without requiring manual operator intervention. These automated responses become essential when dealing with swarm attacks or coordinated multi-drone intrusions where human operators cannot process targeting information quickly enough to prevent successful penetration of protected airspace. Advanced systems can simultaneously track and engage multiple targets using arrays of directional antennas operating under centralized control.
Adaptive Frequency Management
Modern drone manufacturers continuously evolve their communication protocols and frequency management strategies to overcome jamming attempts, requiring directional antenna systems to incorporate adaptive response capabilities. Software-defined radio technology enables directional antenna systems to rapidly scan multiple frequency bands, identify active drone communication channels, and concentrate jamming energy on the specific frequencies used by detected targets rather than broadcasting across entire frequency ranges.
This adaptive approach maximizes jamming effectiveness while minimizing power consumption and reducing interference to nearby communication systems. The system can automatically adjust transmission parameters based on real-time signal analysis, increasing power levels when engaging distant targets or reducing output when dealing with nearby threats. Machine learning algorithms increasingly support these adaptive responses, enabling systems to recognize specific drone models and automatically apply optimal jamming parameters based on historical engagement data and manufacturer communication protocols.
Cost-Effectiveness and Resource Optimization
Reduced Power Requirements and Operating Costs
The focused energy delivery provided by directional antennas enables significant reductions in transmitter power requirements compared to omnidirectional systems attempting to achieve similar effective ranges. Lower power consumption translates directly to reduced operating costs, extended battery life for portable systems, and decreased cooling requirements for fixed installations. These efficiency gains become particularly important for facilities requiring continuous counter-drone protection where energy costs represent a substantial portion of overall security budgets.
The power efficiency advantages extend beyond direct energy savings to encompass reduced infrastructure requirements for electrical distribution, backup power systems, and thermal management equipment. Facilities can often implement effective directional antenna systems using existing electrical infrastructure without requiring costly upgrades to support high-power omnidirectional transmitters. This reduced infrastructure burden enables rapid deployment of counter-drone capabilities at locations where extensive construction projects would be impractical or prohibitively expensive.
Maintenance and Lifecycle Considerations
Directional antenna systems typically demonstrate superior reliability and longevity compared to high-power omnidirectional alternatives due to their reduced thermal stress and lower component wear rates. The concentrated signal delivery approach enables achievement of required performance levels using more conservative component ratings, resulting in extended service life and reduced maintenance requirements. Professional-grade directional antennas often operate reliably for decades with minimal servicing beyond periodic cleaning and connection inspection.
The modular design common to most directional antenna systems facilitates selective component replacement and performance upgrades without requiring complete system replacement. As drone technology evolves and new communication protocols emerge, operators can often maintain effectiveness by updating software parameters, replacing specific RF components, or adding supplementary frequency modules rather than purchasing entirely new counter-drone systems. This upgrade flexibility protects long-term investment values while ensuring continued effectiveness against emerging aerial threats.
FAQ
What frequency ranges do directional antennas typically cover for drone jamming applications?
Most directional antennas designed for drone jamming applications cover the primary frequencies used by commercial drones, including 2.4 GHz and 5.8 GHz ISM bands for control links, plus 1.2 GHz and 1.5 GHz ranges for GPS navigation signals. Professional systems often include additional coverage for 433 MHz, 868 MHz, and 915 MHz frequencies used by specialized industrial drones and older consumer models. The specific frequency selection depends on regional regulations and the types of drones commonly encountered in the operational environment.
How does weather affect directional antenna performance in outdoor installations?
Weather conditions can impact directional antenna performance through various mechanisms including rain attenuation at higher frequencies, ice accumulation affecting beam patterns, and thermal expansion altering mechanical alignment. Professional installations typically incorporate weather-resistant radomes and heating elements to maintain consistent performance across seasonal variations. Rain fade becomes more significant above 10 GHz, but most drone jamming frequencies below 6 GHz experience minimal weather-related signal loss under typical precipitation conditions.
Can directional antennas be detected by sophisticated drone operators using counter-surveillance equipment?
While directional antennas produce more focused electromagnetic signatures than omnidirectional systems, sophisticated adversaries equipped with spectrum analyzers or direction-finding equipment may still detect active jamming operations. However, the narrow beam pattern makes detection more difficult since monitoring equipment must be positioned within the antenna's main lobe to receive strong signals. Operational security can be enhanced through techniques such as frequency hopping, power modulation, and strategic antenna positioning to minimize detection probability while maintaining effectiveness against target drones.
What are the typical engagement ranges achievable with high-gain directional antennas?
Engagement ranges for directional antenna systems vary significantly based on antenna gain, transmitter power, frequency band, and environmental conditions. Professional systems with high-gain directional antennas typically achieve effective ranges of 1-3 kilometers against most commercial drones, with some specialized systems capable of engagement at distances exceeding 5 kilometers under optimal conditions. Range performance depends heavily on the specific drone model being targeted, as aircraft with more sensitive receivers or weaker communication links can be disrupted at greater distances than military-grade platforms with robust anti-jamming capabilities.
Table of Contents
- Technical Advantages of Directional Antenna Systems
- Operational Benefits in Real-World Applications
- Integration with Comprehensive Security Systems
- Cost-Effectiveness and Resource Optimization
-
FAQ
- What frequency ranges do directional antennas typically cover for drone jamming applications?
- How does weather affect directional antenna performance in outdoor installations?
- Can directional antennas be detected by sophisticated drone operators using counter-surveillance equipment?
- What are the typical engagement ranges achievable with high-gain directional antennas?

